Search engine optimization does not require a professional. Most of the work can be done in-house by companies with small to medium-sized websites and e-commerce platforms that are SEO-friendly. Here are our top 10 DIY SEO tips for you.
1. Research keywords
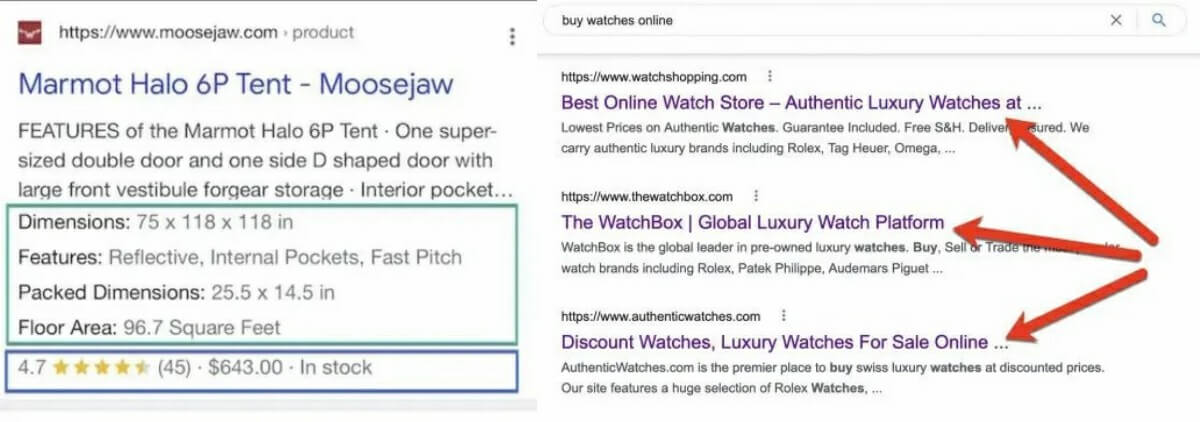
The benefits of keyword research are twofold. First, by discovering and organizing relevant search queries, you’ll learn the words and phrases consumers use to find your products and services. You can then use these keywords in product descriptions, titles, and blog posts—all of which can improve your organic search rankings.
But keyword research isn’t just for SEO. Understanding how consumers search for their needs can uncover competitors (ranking for those keywords) and generate ideas for new or improved products.
There are quite a few free and freemium keyword research tools out there. Organizing keywords by common intent can be challenging (and time-consuming), but it’s doable using a spreadsheet.
2. Determine keyword gaps
A keyword gap is a search query for which two or more of your competitors rank higher but your site does not rank. Advanced tools like Ahrefs and Semrush can identify those missing keywords that represent opportunities for your brand.
The entire analysis process takes no more than 30 minutes. You’ll end up with new content ideas, new pages to create, and popular information queries to solve.
3. Build internal links
Internal links are key to the organic visibility of important pages. Google uses links to crawl websites. Its algorithm assigns equity to each page based on the number of internal links pointing to it.
Google provides no guidance on internal links or where they should reside. But Googlers have been hinting at priorities for years:
- Main navigation.
- Within content, such as the body of a blog post.
- footer.
- Above the fold (top of page).
- Sidebar.
An internal linking strategy should include all of these locations for variety. Use the “Related”, “Top” and “Top” content widgets and make sure your key pages are linked directly from the main navigation or with just a click or two.
4. Increase click-through rate
While keyword research can identify ranking opportunities, click optimization can generate more traffic from existing positions.
My favorite click strategy is rich and structured snippets. Both stand out on search engine results pages. They require minimal coding using Schema.org markup or similar markup. Third-party plug-ins make the job easier.
5. Optimize title tags
Title tags are slowly losing organic ranking power, but they are still important. Including keywords in the title lets Google know the purpose of the page. Additionally, a well-crafted title is probably the most obvious part of a standard search result snippet. Therefore, it also affects click-through rates.
6. Create useful content
Knowing your page’s main keywords and including them in the title (and body text, if that makes sense) is a key component of optimizing your content. But the most important strategy is to create truly useful information that consumers want to consume. Ultimately it’s impossible to optimize content that no one wants to read or view.
Google now understands searcher intent and the relevance and value of content. But it all starts with useful content that serves your target consumers and answers the questions they show up in their search queries.
7. Update old content
Most content slowly loses organic traffic. Older content generates fewer clicks from organic results, primarily due to the date in the search snippet. Additionally, Google is working hard to bring out newer content.
However, you can recoup much of this loss by updating it with new data, new references, contemporary descriptions, and so on.
8. Monitoring and analysis
Google Analytics and Search Console are critical to understanding organic search performance. They report on the pages with the most organic traffic, the keywords driving the traffic, the engagement and conversion rates of the traffic, and many other metrics.
Without access to detailed reports, at least regularly check your analytics for traffic drops or website performance glitches. Both require immediate attention.
9. Build link equity
Link building is the most challenging SEO task. The work is never done. Google uses backlinks to tell you whether your content is trustworthy. For example, links from reputable news sources can increase trust.
The good news is that link-building can be done in-house. The best link-building strategies again come from quality content that people want to share. Participate in niche communities, meet like-minded people, and reach out to journalists—all of this is legal and possible.
Never pay for links, hire people who pay for links, or manually insert self-service links on other websites. If it’s easily accessible, the link may be useless, or worse.
10. Educate yourself
Finally, there is no substitute for knowledge. Learn SEO. There are many great free resources out there. The Search Engine Roundtable is my favorite source for curated SEO news and advice. Moz’s blog is a great, neat resource.
11. Conclusion
Every online merchant should perform some level of DIY SEO. It saves money and gives you control over your organic rankings. However, some tasks may require professional help. Site speed, structured data, and coding changes are examples. If you need to find the right SEO services, contact Donsafe.